
| gnu | home doc changelog |
| source | gnu toybox busybox minised |
| wiki | english spanish |
- 1974, Bell Labs
- by Lee E. McMahon (43)
- "Stream EDitor"
- line-oriented text processing utility
- based on the scripting features of the interactive editor
ed - part of the POSIX standard, mandatory
cli
sed [OPTION] [SCRIPT] [INPUTFILE]
| -e | –expression | script | inline script |
| -f | –file | file | path to script file |
| -n | –quiet ¦ –silent | output only via the p command | |
| -i | –in-place | inplace edit | |
| -i | –in-place | .bkp | inplace edit, saves old version with the .bkp extension |
| -E ¦ -r | –regexp-extended | enables extended regex, instead of default posix | |
| -u | –unbuffered | flushes output more often | |
| -z | –null-data | separate by NUL characters | |
| -s | –separate | consider files as separate | |
| –sandbox | disable e/r/w commands | ||
| –posix | disable GNU extensions | ||
| –debug | annotate execution | ||
| –follow-symlinks | when doing (-i)nplace editing |
language
#!/usr/bin/env -S sed INPUTFILE -i -f #!/bin/sed -f s/Hello/Hell/g
- reads text, line by line, into a temporary buffer called
pattern space - each line read starts a
cycle - there is a special buffer called
hold spaceused by some commands to hold and accumulate text between cycles - check out
man sedor the more completeinfo sed
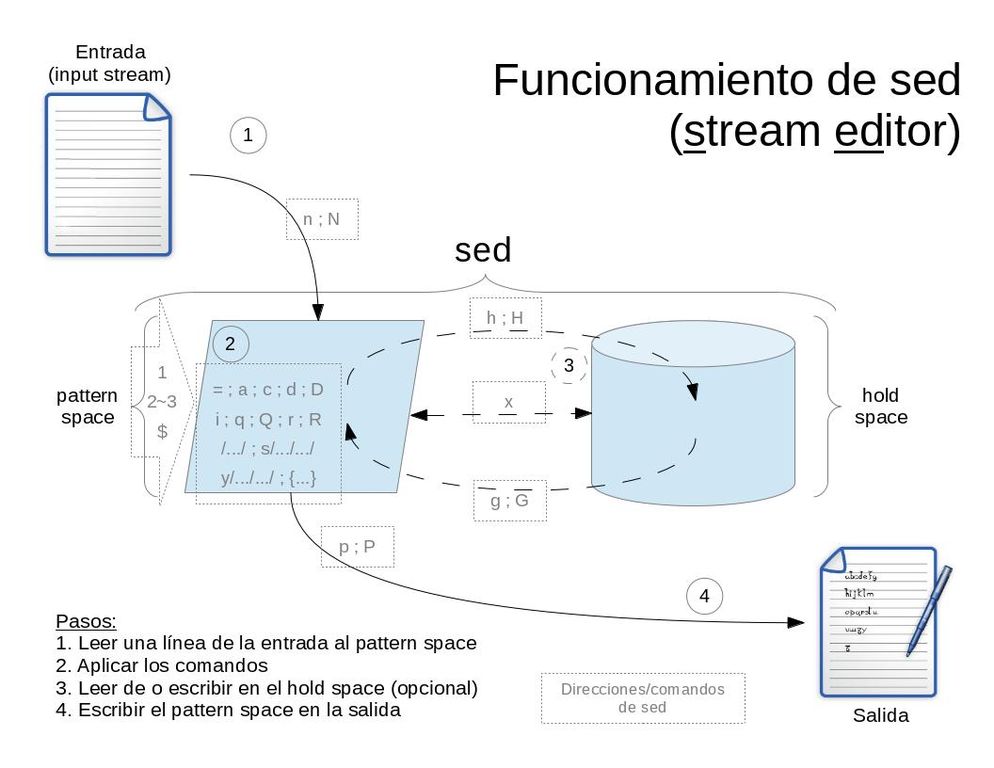
script
- the "body of a loop" that iterates through lines
each line of a script is a pattern-action pair (aka a conditional statement)
[address]command # single command or address { cmd1; cmd2; } # multiple, cannot have a space before ";"
operations
- made of commands
- applied over the pattern space
- by default, after the operations runs
- sed outputs the pattern space
- and begins the cycle again with the next line
addresses
| mnemo | applied to | |
|---|---|---|
| empty | all lines | |
| N | line | line N (of each file) |
| addr! | not | inverses address match |
| N,M | range | from N upto M |
| N~S | stepped | from N upto infinity, with steps of size S |
| N,+L | length | from N upto N+L |
| $ | last | last line |
| regex | match | lines that match regex |
- line numbers start at 1(one)
- can mix-up line number and regex
- aregex
- supports arbitrary characters as delimitators, with a backslash for the left one
- \:aregex:
commands
- there are 25 commands
- optional
address - use {} to apply many commands to the same
address - separate commands with either
- new lines
- cmd1;cmd2
- -e cmd2 -e cmd2
| q [CODE] | quit | exit with optional return CODE |
| z | zap | empties the pattern space (GNU) |
| d | delete | empties the pattern space, and starts a new cycle |
| D | delete | if pattern space drop 1st line if many, else starts a new cycle |
| n | next | reads next line into the pattern space AND prints its old value |
| N | next | appends next line into the pattern space in a new line |
| p | the pattern space | |
| P | the 1st line on the pattern space | |
| = | prints the current line number plus a new line | |
| y/src/dst/ | (tr)ansliterates src chars for dst chars | |
| l | list | list the pattern space unambigously, nice for debugging |
| a STR | append | string after current pattern space |
| i STR | insert | string before current pattern space |
| c STR | change | replaces current pattern space with a given STR |
| s/p/r/f | substitute | /pattern/replacement/flags |
| uses address for pattern if missing | ||
| replacement: "&" pattern matched, \N where N is the N-match group | ||
| flags: [w FILE, g, p, I, NUMBEROFMATCH] | ||
| hk | ||
| e [CMD] | execute | given shell CMD, and stores its output in the pattern space (GNU) |
| r FILE | read | given file and prints it into stdout |
| w FILE | write | pattern space to given file |
| W FILE | write | pattern space to given file, but only the 1st line (GNU) |
| b | bail | jump to the end of the script |
| b LABEL | branch | jump to given tag |
| t LABEL | test branch | jump to given tag, IF previous substitution succeded |
| T LABEL | test branch | jump to given tag, IF previous substitution failed |
| h | hold | copy pattern -> hold |
| H | hold | append \npattern -> hold |
| g | get | copy hold -> pattern |
| G | get | append \nhold -> pattern |
| x | exchange | aka swap content between hold space and pattern space |
snippets

| flag | description | |
|---|---|---|
| p | prints every line twice | |
| p | -n | prints every line |
| 1p | -n | prints first line |
| $p | -n | prints last line |
| 1,3p | -n | prints lines 1 through 3 |
| 20,$p | -n | prints from line 20 to end |
| #,$p | -n | remove before comment (#) |
| =;n | interleaves printing line number, every 2 numbers (1,3..) and each line | |
| $= | -n | prints the number of lines (slow?) |
| $a 8.8.8.8 google.com | -i /etc/hosts | appends ip/hostname at the end |
| 1i #Managed by sed | -i /etc/hosts | inserts before line 1, a comment |
| $d | -i /etc/hosts | deletes last line |
| 2d | delete line 2 | |
| 1,10d | remove the first 10 lines | |
| /^ /d | filters out lines starting with space | |
| /^ *$/d | filters out lines containing only spaces | |
| 50,$d | deletes from line 50 to the end | |
| /needle/d | deletes lines containing "needle" | |
| 1,/^$/d | deletes from 1st line to the first blank line | |
| /^(#¦$)/d | -E | remove comments and empty lines |
| /^#/d;/^$/d | remove comments and empty lines | |
| /^\s*(#¦$)/d | -E | remove comments, indentend comments, and empty lines |
| ---!s/–/\\(em/g | on all lines that do not have 3(-), replace 2(-) | |
| s/.*/Hello/;q | reads 1st line of input and prints "Hello" | |
| s/needle//g | deletes "needle" from lines | |
| s/.$// | dos2unix, aka CRLF to LF | |
| /ant/s/needle//g | delete needle on lines containing "ant" | |
| 1,/^.//./!d | delete all leading empty lines | |
| :x;/./!{N;s/^\n$//;tx} | on an empty line, remove all empty, but one |
remove the last 15 lines of a file
$ sox -r 22100 -t u16 -c 1 icerok.raw -n stat -freq 2>&1 |
sed -n -e :a -e '1,15!{P;N;D;};N;ba' |
gnuplot -p -e 'set logscale x; plot "-" with l'
gotchas
- does NOT follow symlinks for inplace edit by default, unless
--follow-symlinks
codebases

trivia
"Blame Lee E. McMahon for sed's syntax. :-)"
- This comment is added by a template in each "configure" generated by autoconf
- 30k matches in github, present on android, gmp, chromium, racket, distcc,…
Added by Paul Eggert in 2001
# Create $as_me.lineno as a copy of $as_myself, but with $LINENO # uniformly replaced by the line number. The first 'sed' inserts a # line-number line before each line; the second 'sed' does the real # work. The second script uses 'N' to pair each line-number line # with the numbered line, and appends trailing '-' during # substitution so that $LINENO is not a special case at line end. # (Raja R Harinath suggested sed '=', and Paul Eggert wrote the # second 'sed' script. Blame Lee E. McMahon for sed's syntax. :-) sed '=' <$as_myself | sed ' N s,$,-, : loop s,^\([[0-9]]*\)\(.*\)[[$]]LINENO\([[^a-zA-Z0-9_]]\),\1\2\1\3, t loop s,-$,, s,^[[0-9]]*\n,, ' >$as_me.lineno && chmod +x $as_me.lineno || AS_ERROR([cannot create $as_me.lineno; rerun with a POSIX shell])